Welcome To Homestead Inspiration
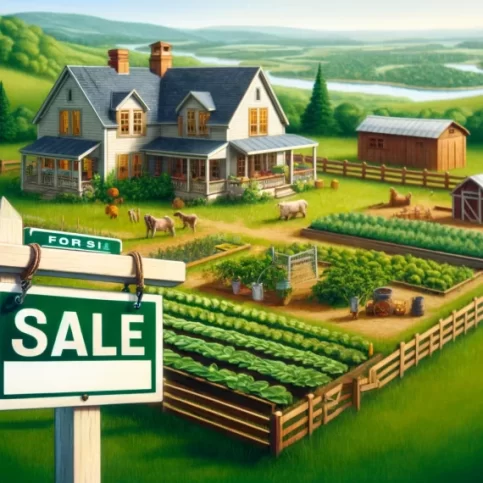

Where to Find Homesteading Land for Sale?
Finding the right land for homesteading is a crucial step in starting your self-sufficient lifestyle..
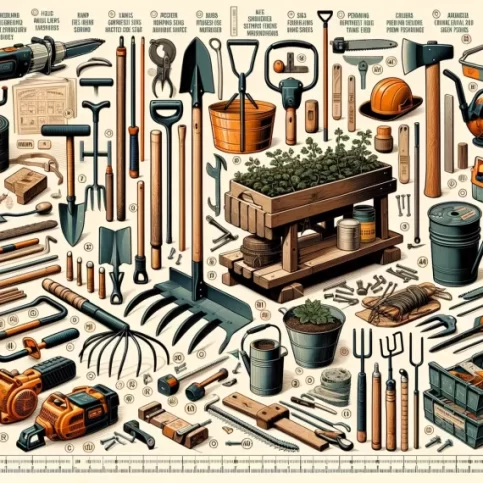

What are Essential Tools for Homesteading?
Homesteading involves a wide range of activities, from gardening and raising livestock to food preservation.
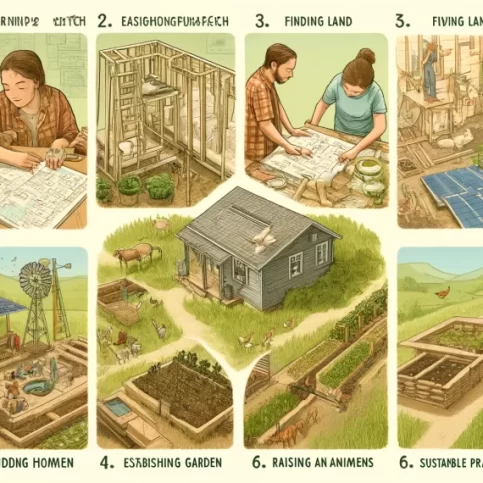

How to Start Homesteading?
Starting a homestead can be a rewarding journey toward self-sufficiency and sustainability. Here’s a guide.
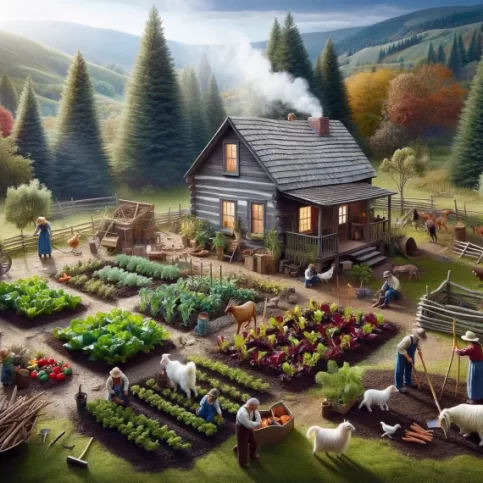

What Is Homesteading?
Homesteading is a lifestyle of self-sufficiency, characterized by subsistence agriculture, home preservation of food, and.

Budget-Friendly Tips for Novice Homesteaders
Starting a homestead can be financially daunting, but with careful planning and resourcefulness, it is.
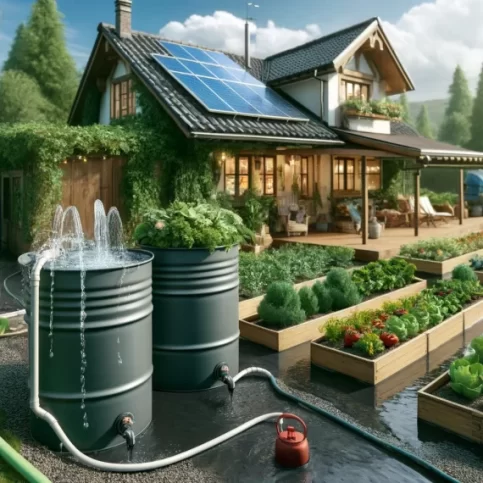

Eco-Friendly Practices for Homesteading
Eco-friendly practices for homesteading benefits and guidelines Incorporating eco-friendly practices into homesteading is essential for.

Raising Chickens Resources
Useful Further Reading Mother Earth News - A comprehensive guide on various aspects of raising.
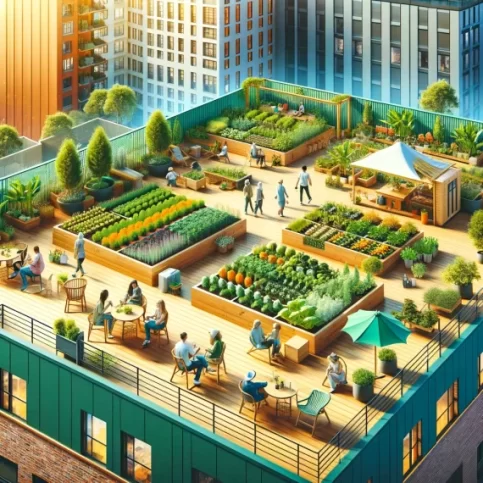

Urban Gardening
Urban community rooftop gardens offer numerous benefits, enhancing both environmental sustainability and social well-being. These.
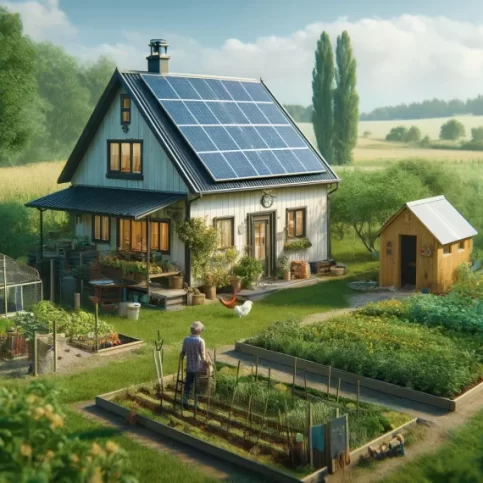
DIY Homesteading
DIY homesteading offers numerous benefits, promoting self-sufficiency and sustainable living. Homesteaders grow their own food,.
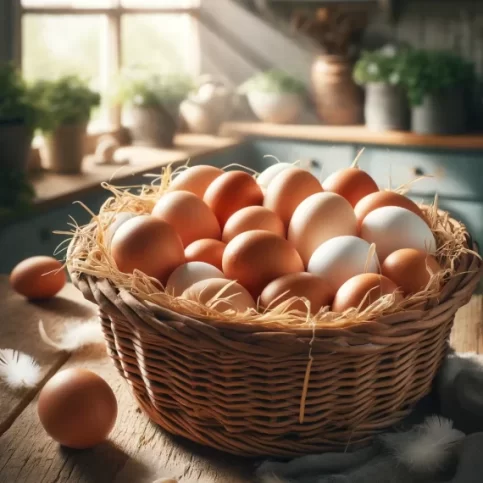

Benefits of Chickens
Raising backyard chickens provides numerous benefits, primarily through the production of fresh, nutritious eggs. These.
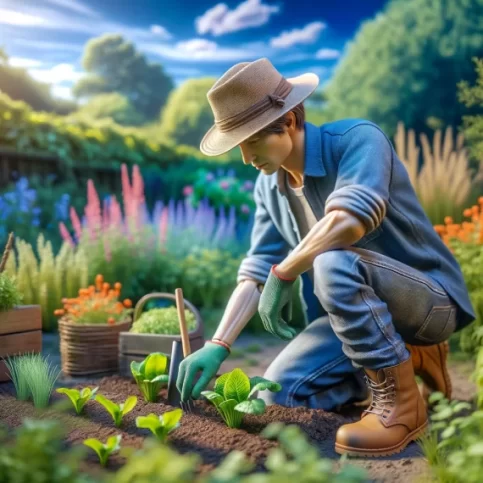

Gardening Resources
Learn more about backyard gardening, consider the following resources: Books and Guides: Look for books.
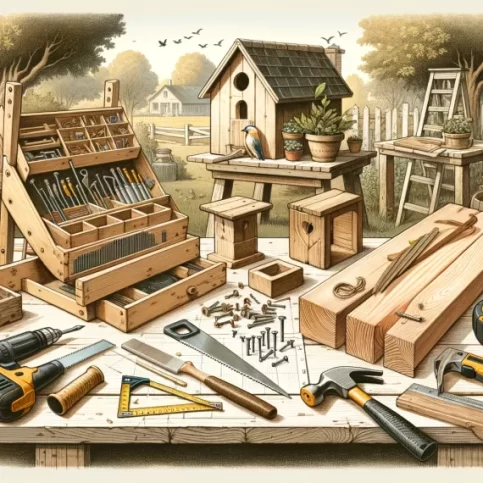

DIY Homesteading Resources
Sources that could be helpful for your DIY homestead project: Gardening Association: The National Gardening.

Homesteading Ideas Resources
General Tips Research Extensively: Before starting any project, gather as much information as possible to.
The Ultimate Guide to Off-Grid Living: Achieve Self-Sufficiency with Homestead Inspiration
Off-Grid Living Made Simple
Off-grid living is an exciting journey towards self-sufficiency and sustainability. Whether you are just starting out or looking to improve your homestead, Homestead Inspiration provides beginner-friendly resources, local community building initiatives, and a holistic sustainability approach to help you every step of the way. In this guide, we explore essential off-grid living concepts to help you make informed decisions and successfully transition into a self-sufficient lifestyle.
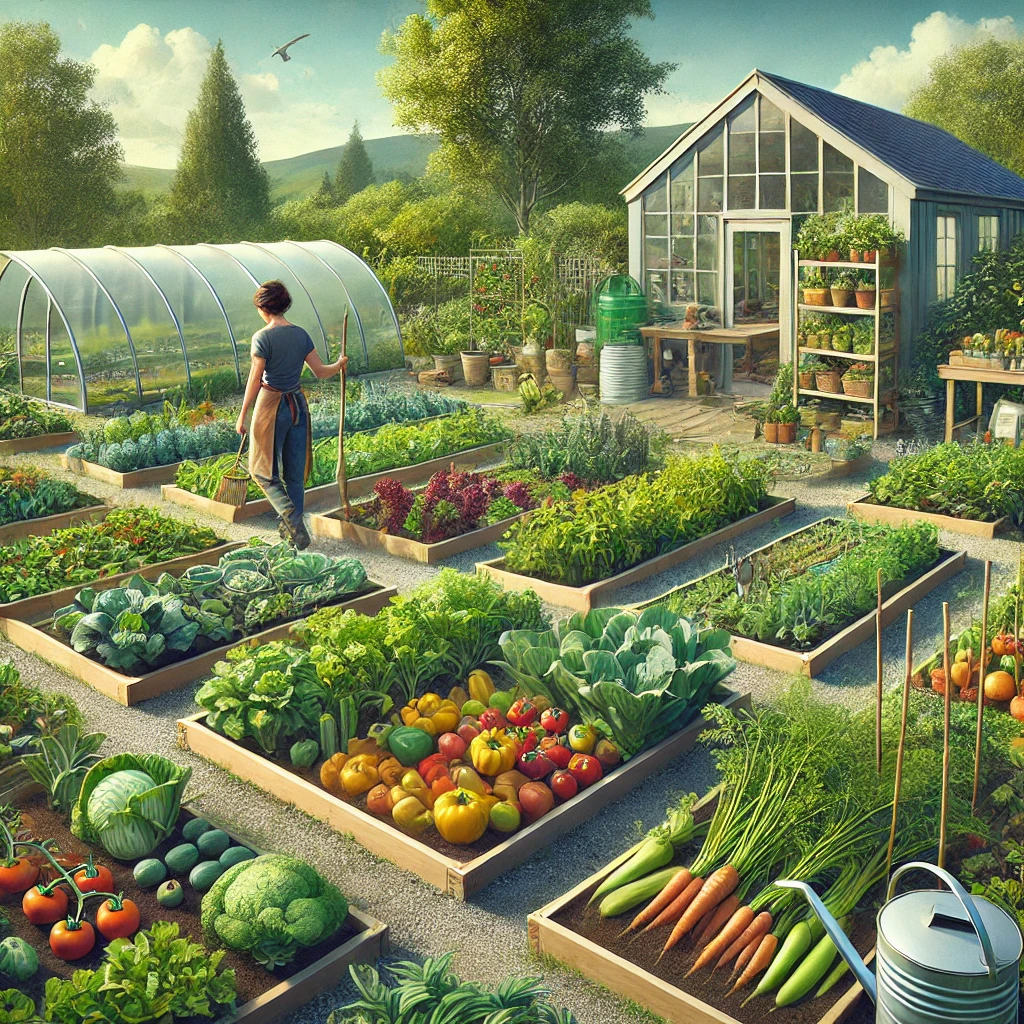

1. Food Production
Growing Your Own Food for a Sustainable Future
Food production is the foundation of off-grid living. Growing your own vegetables, fruits, and herbs ensures access to fresh, organic food while reducing dependency on grocery stores.
Key steps to start:
- Choose nutrient-rich soil and organic compost for planting.
- Grow seasonal vegetables and fruits to ensure a steady supply of food.
- Use raised beds, container gardening, or hydroponics for efficient space usage.
Homestead Inspiration provides detailed guides and starter kits to help you set up your food production system efficiently.

📌 Resource: Food Production Guide
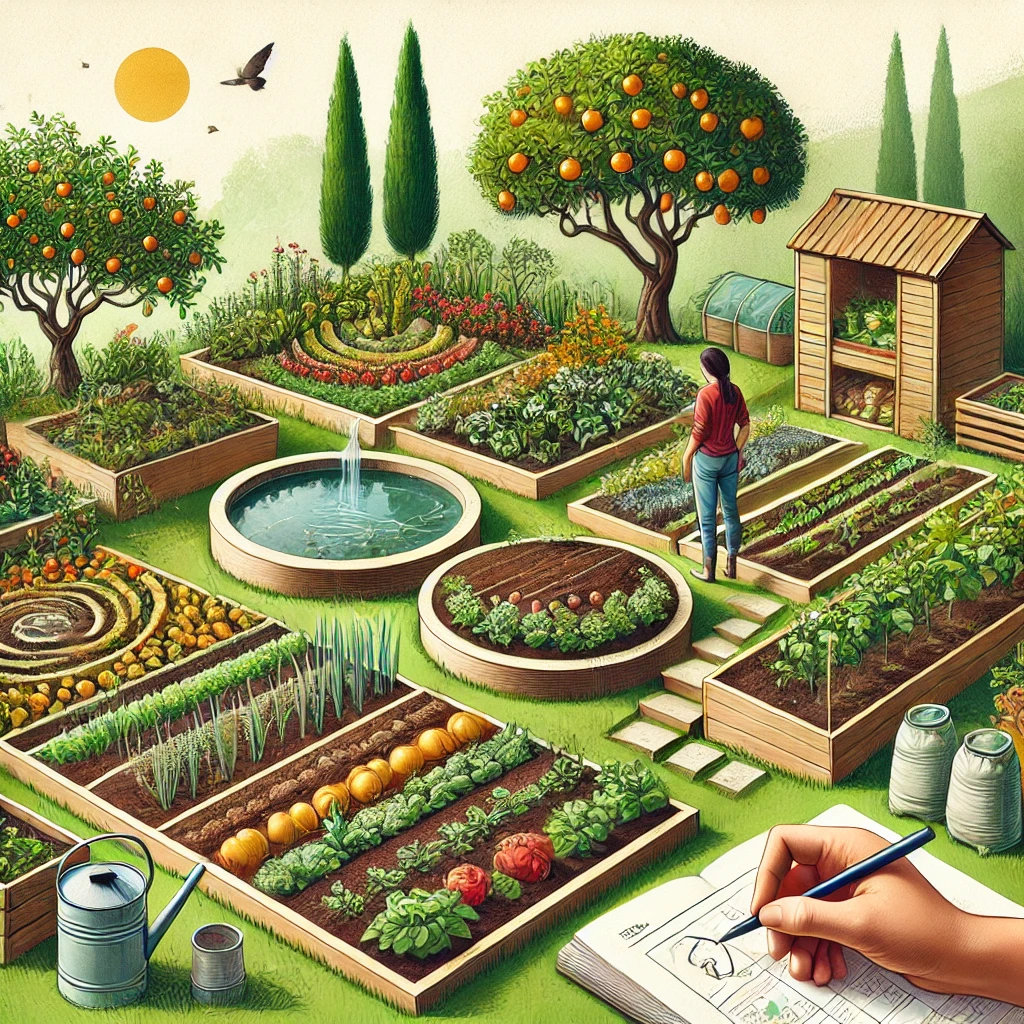

2. Permaculture Design
Building a Self-Sustaining Ecosystem
Permaculture design focuses on creating a self-sustaining ecosystem that works in harmony with nature. By mimicking natural processes, you can cultivate a productive and resilient landscape.
Key techniques include:
- Companion planting to boost soil fertility and deter pests.
- Rainwater harvesting for irrigation and sustainability.
- Creating food forests to enhance biodiversity.
Homestead Inspiration offers hands-on permaculture workshops and expert-led tutorials to guide you through the process.
📌 Resource: Permaculture Design Guide
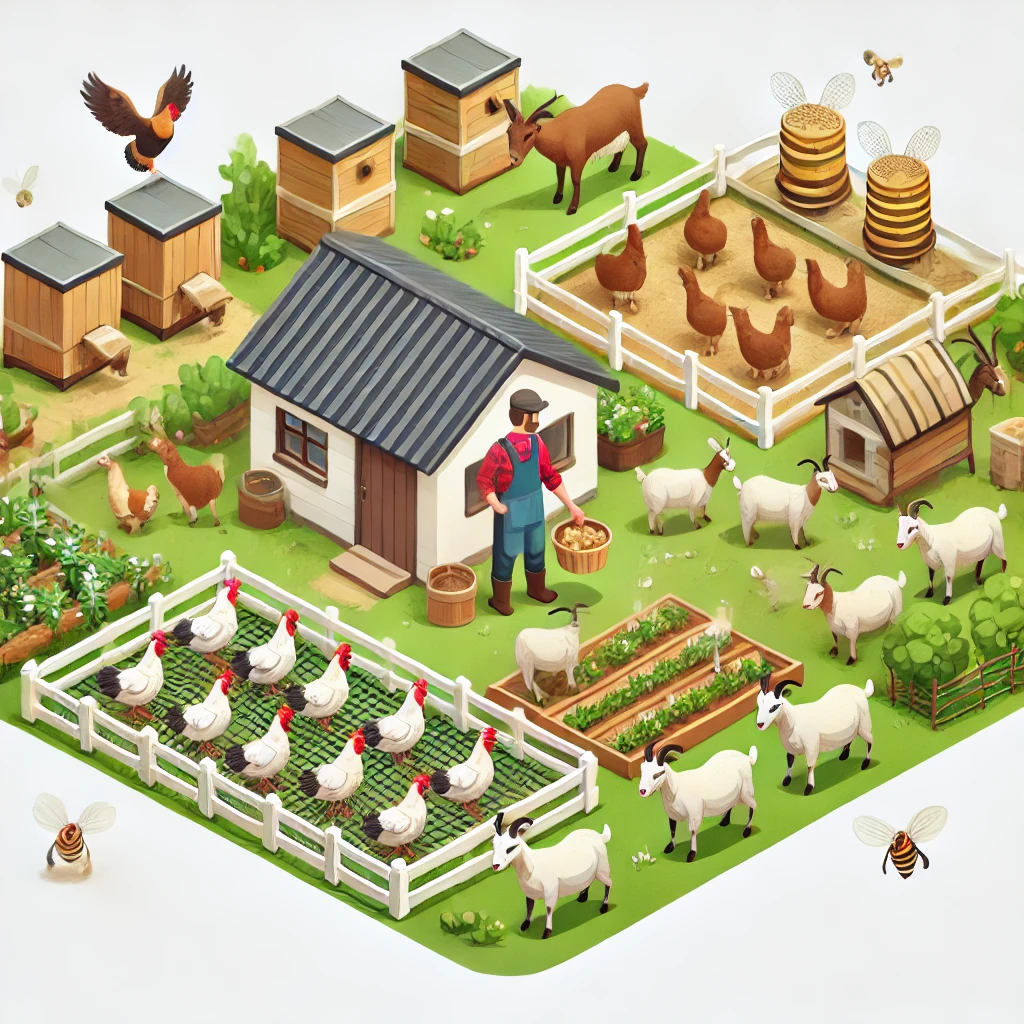

3. Animal Husbandry
Raising Livestock for Self-Sufficiency
Animal husbandry plays a crucial role in off-grid living, providing fresh eggs, milk, meat, and natural fertilizers. Whether you choose to raise chickens, goats, or bees, proper care is essential.
Key considerations:
- Select livestock that suits your land size and climate.
- Provide adequate shelter, food, and water for healthy growth.
- Implement rotational grazing to prevent overgrazing and improve soil health.
Homestead Inspiration connects you with local farmers and livestock experts to ensure you have the best guidance on raising animals responsibly.
📌 Resource: Animal Husbandry Guide
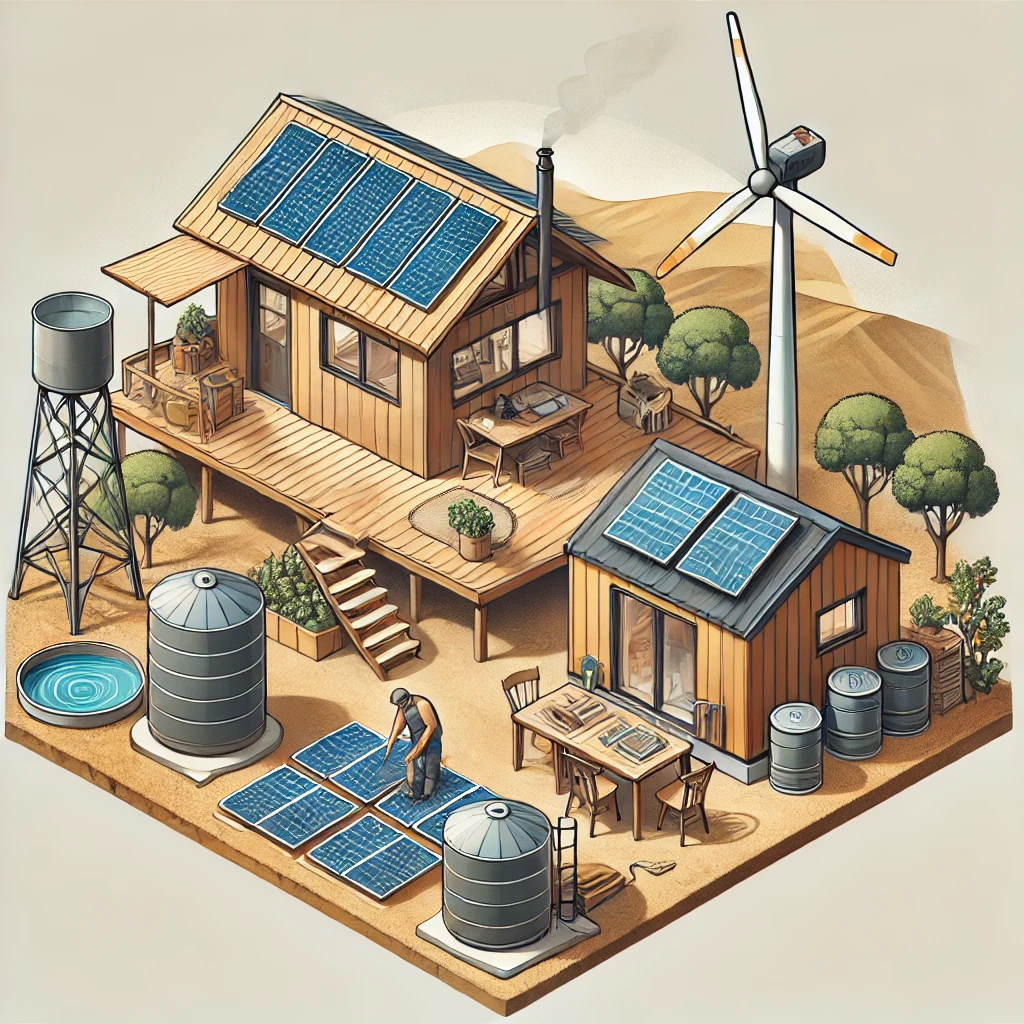

4. Shelter and Infrastructure
Building Sustainable and Efficient Living Spaces
Creating a functional and sustainable home is essential for off-grid living. From tiny homes to earth-sheltered houses, designing an eco-friendly shelter reduces energy consumption and maximizes resource efficiency.
Key elements include:
- Utilizing solar panels, wind turbines, or micro-hydro power for electricity.
- Implementing passive solar design to reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Using recycled or natural materials for construction.
Homestead Inspiration offers affordable DIY home-building kits and expert consultations to help you build a durable and efficient off-grid home.
📌 Resource: Shelter & Infrastructure Guide
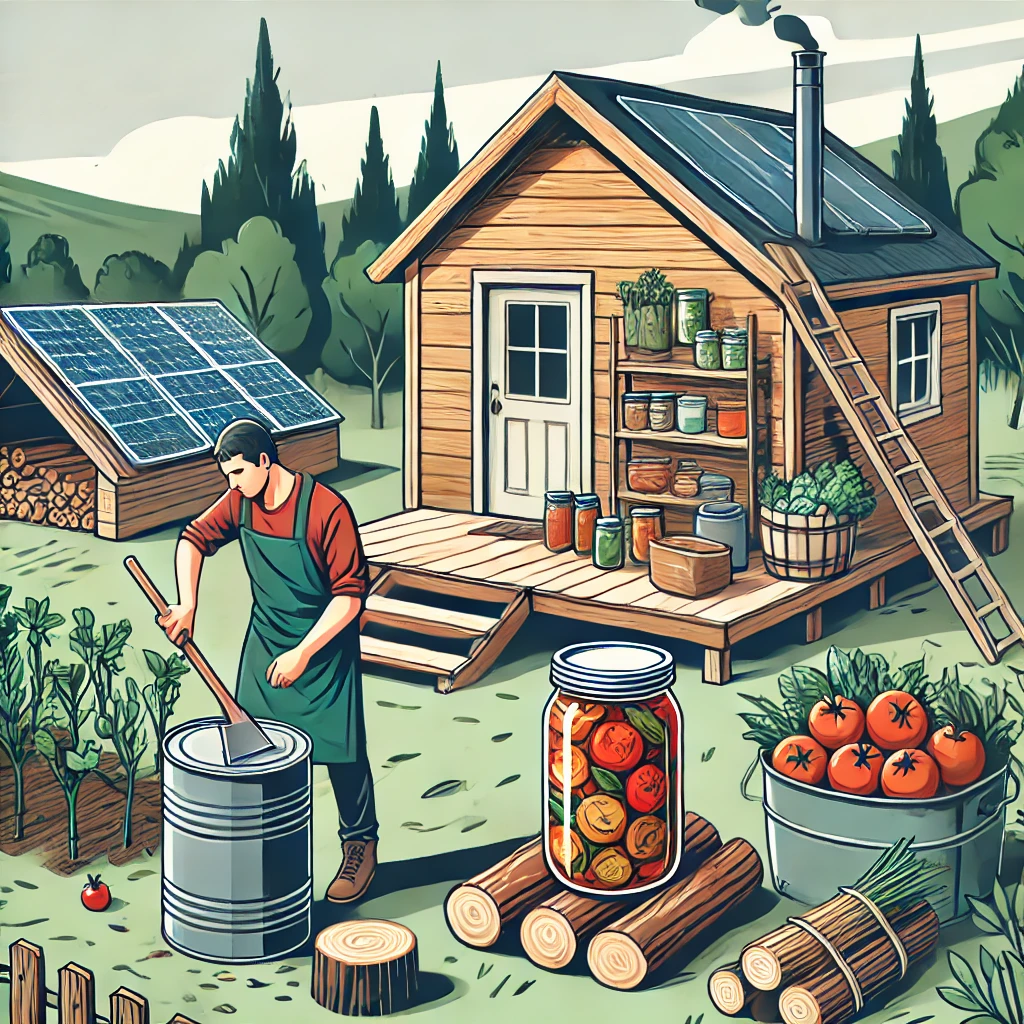

5. Self-Sufficiency Skills
Essential Skills for Living Off the Grid
To thrive in an off-grid lifestyle, developing self-sufficiency skills is essential. These skills ensure you can maintain your homestead independently and prepare for unexpected situations.
Must-have skills include:
- Food preservation methods such as canning, fermenting, and dehydrating.
- DIY repairs for plumbing, carpentry, and mechanical systems.
- First-aid training for emergencies and basic healthcare needs.
Homestead Inspiration provides hands-on workshops and online courses to help you master these essential skills and gain confidence in off-grid living.
📌 Resource: Self-Sufficiency Skills Guide
Start Your Off-Grid Journey with Homestead Inspiration
Off-grid living is not just about survival—it’s about thriving. With Homestead Inspiration, you gain access to expert resources, a supportive community, and proven strategies to build a sustainable and independent lifestyle.
👉 Start today by exploring our guides, connecting with local homesteaders, and taking control of your self-sufficient future!
Ready to Begin? Join the Homesteading Community Today!
Homesteading News
Farming for Beginners Why Homestead
Farming for Beginners Video - Why You Should Homestead Homesteading or farming for beginners is.






